Vision-based automatic counting and packaging machines: An important tool for improving production efficiency and accuracy.
In today's rapidly developing industrial sector, visual counting automatic packaging machines have become a highly efficient and accurate counting tool, widely used in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. This machine utilizes advanced image processing technology, capturing product images with high-resolution cameras, then using software for precise counting, and automatically packaging the counted products. This article will detail the working principles, features, and advantages of visual counting automatic packaging machines, as well as their application cases in various industries.
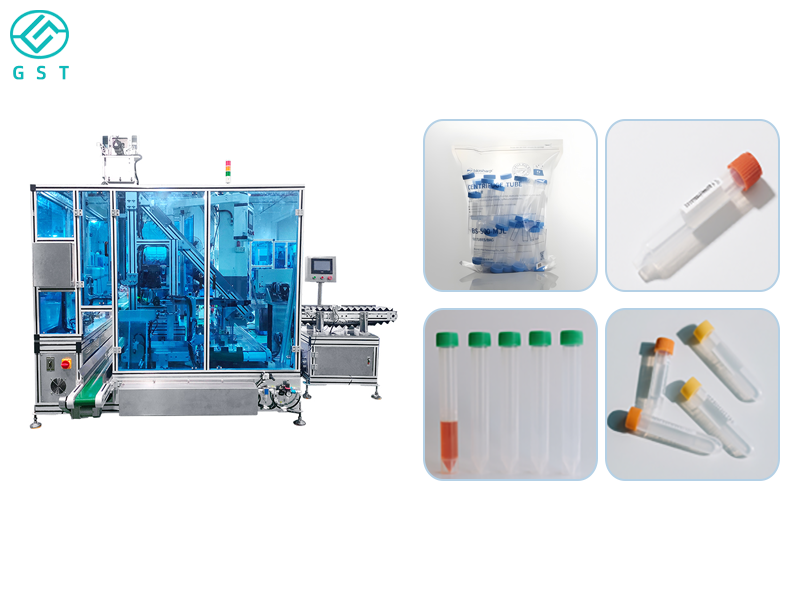

Working Principle of Visual Counting Automatic Packaging Machines
A visual counting automatic packaging machine mainly consists of three parts: image capture, image processing, and packaging execution. First, a high-resolution camera captures product images, which are then transmitted to the image processing unit. The image processing unit contains one or more high-speed computers that convert the images into digital signals and perform counting using specialized software. Finally, based on the counting results, the packaging execution part packages the products into the designated containers.
Features and Advantages of Visual Counting Automatic Packaging Machines
Compared with traditional counting methods, visual counting automatic packaging machines have the following features and advantages:
High Efficiency: Visual counting automatic packaging machines can complete counting tasks quickly and accurately, greatly improving production efficiency.
Accuracy: Using image processing technology for counting effectively reduces human error and improves counting accuracy.
Wide Adaptability: Visual counting automatic packaging machines can adapt to various products of different shapes and sizes without requiring significant machine adjustments.
Automation: Visual counting automatic packaging machines can achieve an automated packaging process, reducing labor costs and improving the level of production automation.
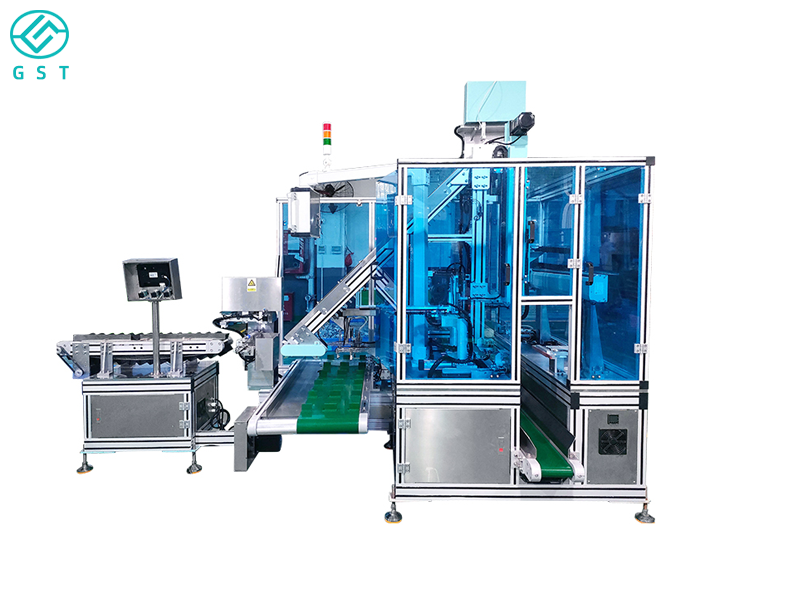

Application Cases of Visual Counting Automatic Packaging Machines
Food Industry: In the food industry, visual counting automatic packaging machines are widely used for counting and packaging small food items such as candies, chocolates, and nuts. After a chocolate manufacturer adopted a visual counting automatic packaging machine, they not only improved production efficiency but also ensured counting accuracy, significantly reducing the errors that occurred with previous manual counting.
Pharmaceutical Industry: In the pharmaceutical industry, accurate counting and packaging of medicines are crucial. A pharmaceutical company uses a vision-based automatic counting and packaging machine for counting and packaging capsules, which not only improves production efficiency but also ensures the safety and hygiene of the pharmaceuticals.
Chemical industry: In the chemical industry, accurate counting and packaging of various chemical raw materials are crucial for quality control in the production process. After a chemical plant adopted a vision-based automatic counting and packaging machine for counting and packaging chemical raw materials, it significantly improved production efficiency and reduced the impact of human error on product quality.
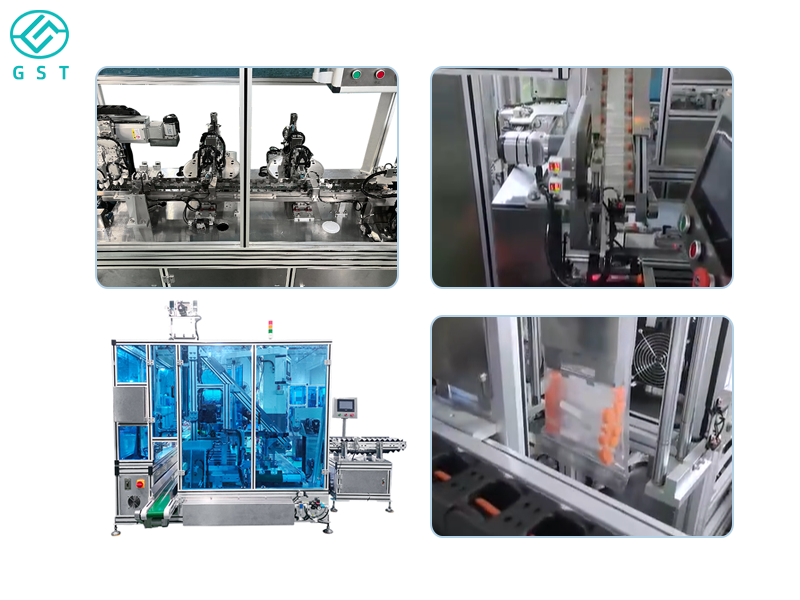
Vision-based automatic counting and packaging machines, as advanced automated equipment, have been widely used in various industries. They utilize image processing technology and offer advantages such as high efficiency, accuracy, strong adaptability, and automation. By using vision-based automatic counting and packaging machines, companies can improve production efficiency, reduce costs, minimize human error, and enhance product quality and safety. With continuous technological advancements, vision-based automatic counting and packaging machines will be applied and developed in more fields, bringing greater convenience and benefits to modern industrial production.